- Science of Glycochemistry
- GlycoSMART Platform
- Product Pipeline
- Publications
Science of Glycochemistry
Small fragments derived from natural polysaccharides : similar activities with several competitive advantages
Polysaccharides are the most common biopolymers available in abundance in natural resources. They play significant roles in the biology of living organisms.
Polysaccharides are composed of condensation polymeric chains in which monosaccharide units are linked together through O-glycosidic bonds.
These Polysaccharides can be classified into five groups (figure 1) : plant, marine, microbial, animal, and fungi polysaccharides. They have many uses like Nutraceuticals, Biomedical research, cosmetic, and medical therapeutics.
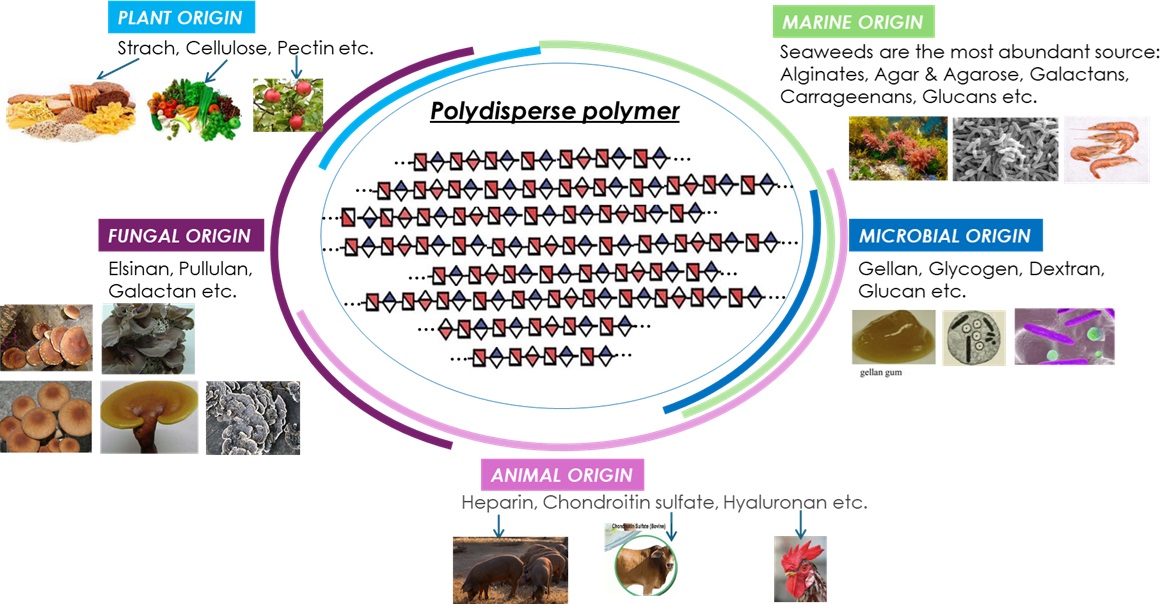
Natural polysaccharides have numerous health-promoting properties such as antitumor, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral, immunomodulatory, hypoglycemic, hepatoprotective, gastrointestinal-protective, antidiabetic properties and more.
The commercially significant polysaccharides such as heparin, chitosan, alginate, dextran, starch, and inulin are primarily obtained from microorganisms, plants, and animals.
Although 30 sugar based drugs are presently on the market for various therapeutic areas (infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, CNS disorders, inflammation, diabetes, thrombosis, etc.), sugars still remain an untapped source of drugs.In addition, saccharides are widely used in cosmetics with anti-inflammation, skin conditioning and moisturizing functions just to name a few.Even if polysaccharide variety is important in nature, the diversity used for therapeutic, veterinary, nutraceutical and cosmetic is quite limited and thus a larger diversity is needed.
It means that new approaches are required which is now possible by using pure, small, and synthetic oligosaccharides designed and produced with CarboMimetics innovative platform GlycoSMART.
Because these small sugars (fragments, oligosaccharides) are derived from natural saccharides, they present several competitive advantages:
- Extension of saccharide variety
- Naturally related molecules, less immunogenic and more human friendly
- New & huge space of patentability
- Possibility to design molecules against non-conventional and difficult targets
- New mode of actions (leaving space for first-in-class)
- Broad possibilities of optimization from initial structures (exclusive to CarboMimetics GlycoSmart)
